Chemical structure
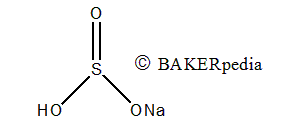
Origin
Sodium bisulfite is commonly obtained by treating an alkali such as sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide with sulfur dioxide.3
Function
Sodium bisulfite has several functions in bakery systems:
- Antibacterial: inhibits the growth of bacteria in high pH and high water activity conditions.
- Antioxidant: reatards oxidation and rancidity, due to its oxygen scavenging properties.
- Retards enzymatic browning reactions: especially in fruit products.
- Reducing agent: improves flour properties by inhibiting the restoration of disulfide bonds, providing a pliable dough.
- Improves dough machinability: by reducing the amount of shrinkage or set back, thus producing uniform crackers.
Nutrition and health
In sensitive individuals, sulfites may pose potential respiratory risk. Acceptable daily intake of sulfites should not exceed 0.7 mg/Kg body weight..3
Sodium bisulfite can reduce vitamin B1 (thiamine) content in meat and fruits.
Commercial production
Sodium bisulfite can be commercially produced through the following process:4
- First reaction: sodium hydroxide and sulfur dioxide are mixed in an aqueous stream to produce sodium sulfite.
- Crystallization: sodium sulfite liquor is introduced into a crystallizer and a purge stream is redirected to be used in the second reaction.
- Second reaction: sulfur dioxide is added to the purge stream to produce sodium bisulfite.
- Second crystallization: sodium bisulfite is crystallized to obtain the solid product.
- Particle reduction and packaging.
Application
Sodium bisulfite can be used in making cookies and biscuits due to its dough conditioning and antibrowning properties. In jams and jellies, it can be used as an antioxidant to prevent color deterioration and as an antimicrobial agent.1,2
When used in baked goods, sodium bisulfite produces the following effects:1,2
- Improves sheeting by reducing shrinkage.
- Improves uniformity of crackers and cookies by reducing set back and inhibiting excessive browning.
- Improves dough texture by inhibiting the restoration of disulfide bonds.
Regulations
Sodium Bisulfite is a substance generally recognized as safe by the FDA, when used under good manufacturing practices.Currently, uses of sodium bisulfite above 10 ppm should be indicated in the label of the product.5
In the EU, Sodium Bisulfite (E 222) is regulated by the EU Commission No 1130/2011, and has a maximum limit of addition to non beverages food products of 2 mg/kg.6
References
- Russell, N. J., and Gould, G.W eds. Food preservatives. Springer Science & Business Media, 2003.
- Hui, Y., Corke, H., De Leyn, I., Nip, W.N and Cross, N .Bakery products: science and technology. John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
- Madhavi, D. L., Deshpande, S.S and Salunkhe, D.K . Food antioxidants: Technological: Toxicological and health perspectives. CRC Press, 1995.
- Kisielewski, J and Robertson,D . “Process for production of sodium bisulfite.” U.S. Patent No. 7,985,396. 26 Jul. 2011.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). US Department of Health and Human Services. CFR Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, Part 182 Substances Generally Recognized as Safe, https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=182.3739 , Accessed 22 December 2020.
- European Commission (Ec). Commission Regulation (Eu) No 1130/2011 Of 11 November 2011 Amending Annex Iii To Regulation (Ec) No 1333/2008 Of The European Parliament And Of The Council On Food Additives By Establishing A Union List Of Food Additives Approved For Use In Food Additives, Food Enzymes, Food Flavourings And Nutrients . Official Journal Of European Communities, 11 November 2011.

